 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Grok
Grok
 Perplexity AI
Perplexity AI
4 min read | By Admin | 25 September 2020 | Frameworks
JVM represents a java virtual machine which is a virtual computing machine or abstract computing machine is the execution of a JVM specification. It explains the bundled Java code called byte code and assists to execute the program depending on the specific stage. Java virtual machine is a platform independent execution milieu which alters machine language into Java byte code and is proficient in implementing byte code. It’s a portion of the Java runtime environment that is required by each operating framework.JVM introduced two revolutionary concepts that became the standard for modern software development, “write once, run anywhere” and automated memory management.The Java Virtual Machine was originally intended only for Java, and today it has been developed to support many programming languages, including Kotlin, Scala, and Groovy.The role of JVM administers system memory and affords a minimal functional environment for Java based applications and still persists to patronage programming innovations today.Let’s know here what is the role and responsibility of JVM in program execution to build an eminent software development.
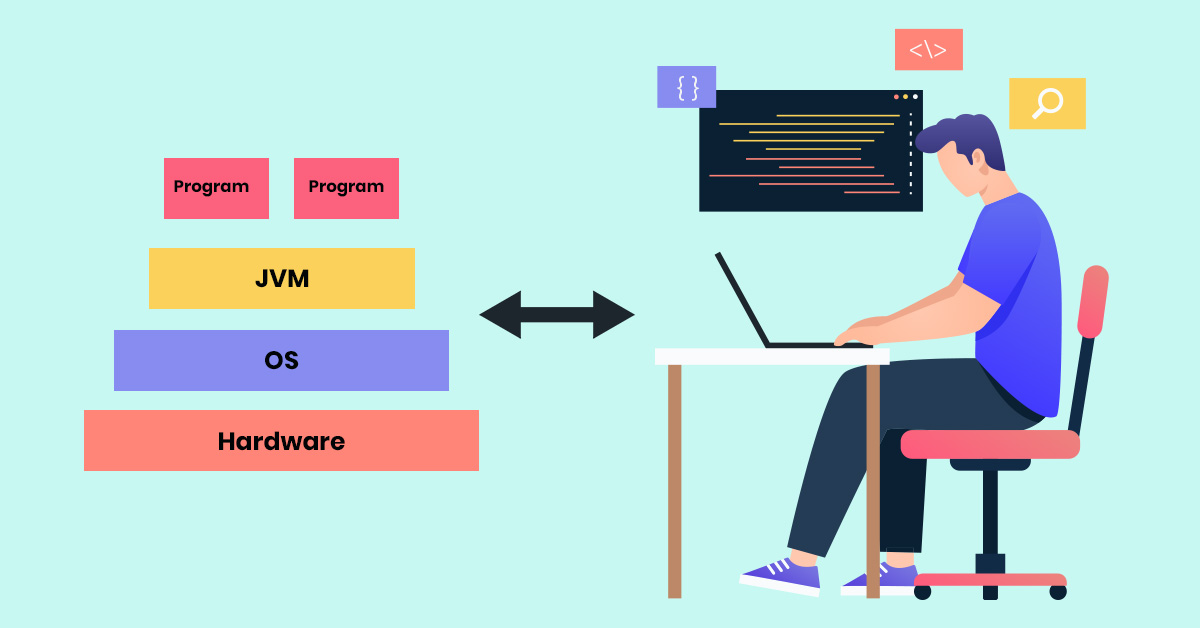
Java is compiled into Java bytecode, which is then translated into a specialized platform by an interpreted Java Interpreter. Actually, this Java interpreter is called Java Virtual Machine. The role of JVM in Java is an abstract machine designed to be implemented on top of existing processors. The purpose of JVM is to provide a runtime environment that enables Java applications to run on any device or operating system without modification. It hides the underlying operating system from Java applications. See below for a comprehensive understanding of JVM’s role in Java.
The role of JVM in Java is an abstract machine designed to be implemented on top of existing processors. It hides the underlying operating system from Java applications.
See below for comprehensive understanding of JVM role in Java.
JVM implies in terms of Java Virtual Machine. It is a specification that bestows a runtime environment in which Java bytecode can be executed and is an abstract machine. Functionality of JVM includes managing memory, executing bytecode, and ensuring platform independence for Java applications. JVM can be implemented in many hardware and software platforms. Also, it has run on both client and server-side platforms. JVM includes a Just-in-Time compiler that converts bytecode into a machine language so that it runs as fast as the native executable. In many programming languages, the compiler generates machine code for a particular system. However, the Java compiler generates the code for a virtual machine, called a JVM.
JVM can be implemented in many hardware and software platforms. Also, it has run on both clients and server-side platforms. JVM includes a Just-in-Time compiler that converts bytecode into a machine language so that it runs as fast as the native executable.
In many programming languages, the compiler generates machine code for a particular system. However, the Java compiler generates the code for a virtual machine, called a JVM.
 𝐓𝐡𝐞 𝐫𝐨𝐥𝐞 𝐨𝐟 𝐉𝐕𝐌 𝐡𝐚𝐬 𝐭𝐰𝐨 𝐦𝐨𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐨𝐮𝐬 𝐜𝐚𝐩𝐚𝐜𝐢𝐭𝐢𝐞𝐬:
𝐓𝐡𝐞 𝐫𝐨𝐥𝐞 𝐨𝐟 𝐉𝐕𝐌 𝐡𝐚𝐬 𝐭𝐰𝐨 𝐦𝐨𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐨𝐮𝐬 𝐜𝐚𝐩𝐚𝐜𝐢𝐭𝐢𝐞𝐬:
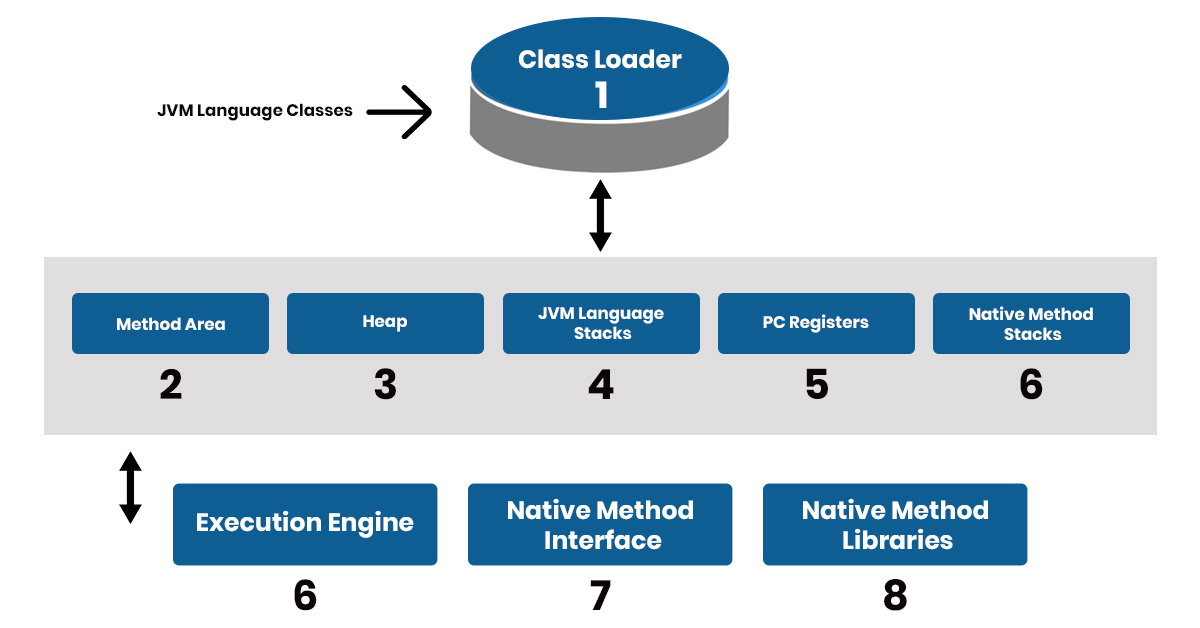

The Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is made up of several key components that enable the execution of Java programs:
𝐂𝐥𝐚𝐬𝐬 𝐋𝐨𝐚𝐝𝐞𝐫: Loads and links Java classes dynamically at runtime
𝐌𝐞𝐦𝐨𝐫𝐲 𝐀𝐫𝐞𝐚𝐬: Divided into different sections for efficient memory management:
●Method Area: Stores class metadata and static variables
●Heap: Allocates memory for objects
●Stack:Handles method execution and local variables
●PC Register: Keeps track of the current instruction
●Native Method Stack: Supports native method execution
𝐄𝐱𝐞𝐜𝐮𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 𝐄𝐧𝐠𝐢𝐧𝐞: Converts bytecode into machine code and executes it using:
●Interpreter:Processes bytecode one instruction at a time
●JIT Compiler:Optimizes performance by converting bytecode to native code
𝐆𝐚𝐫𝐛𝐚𝐠𝐞 𝐂𝐨𝐥𝐥𝐞𝐜𝐭𝐨𝐫: Frees memory by removing unused objects
𝐍𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐯𝐞 𝐈𝐧𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐟𝐚𝐜𝐞:Connects Java applications with native system libraries
These components work together to ensure Java programs run efficiently across different platforms.
JVM, Java Virtual Machine, is a software engine that runs Java programs by converting bytecode into machine code. Significance of JVM lies in its ability to provide platform independence, manage memory efficiently, and optimize execution for better performance.
JVM (Java Virtual Machine) is a software engine that runs Java programs by converting bytecode into machine code. It enables platform independence and manages memory, making Java applications efficient and secure.
Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is an essential part of the Java Runtime Environment. It functions as Java applications as a run-time engine, loading, verifying, and executing Java bytecode, allowing Java applications to run on different operating systems without modification.
JVM performs several key functions, including:
Join over 150,000+ subscribers who get our best digital insights, strategies and tips delivered straight to their inbox.
Comments are closed.