 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Grok
Grok
 Perplexity AI
Perplexity AI

4 min read | By Postpublisher P | 14 November 2022 | Technology
Businesses are constantly striving to optimise their operational efficiency as much as possible. Whether running high-end enterprise applications or storing large amounts of data, businesses are looking for ways to implement new technologies that scale faster.
Enterprises today are looking for optimised solutions for their on-premises data to improve operational efficiency. Since performance is critical, the solution lies in setting up a virtualized data setup through Virtual Machines.
Virtual machines are often used for non-critical purposes, but can be deployed for any computing process your business requires. VMs are primarily used for testing resources, running older operating systems required for legacy systems, designing and testing software, or consolidating servers within an organisation.
Virtual machines are the solution companies need to keep up with technology changes and thrive in today’s competitive work scenarios with finest business operational efficiency. Setting up a virtual machine solution is quick and easy, provided all technical requirements are met. Additionally, businesses can enjoy the many benefits of virtual machines without worrying about the management and technicalities of the same.
Let’s deep drive into this article to know more about virtual machines help to improve operational efficiency.
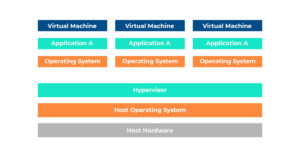
A virtual machine is a computer that runs entirely on software rather than physical hardware. A virtual machine uses software on a physical (host) computer to replicate or emulate the functionality of another computer or operating system. A VM is basically a simulated computer inside a real computer.
A VM provides an isolated environment to run its own operating system and applications, independent of the underlying host system and other VMs on that host. A VM’s operating system is commonly called a guest operating system and can be the same or different from the host operating system or other VMs.
A virtual machine is a computer file, usually called an image, that behaves like a real computer. In many cases, it can be run inside a window as a separate computing environment to run another operating system. It can even function as a user’s computing her experience as a whole, as is common with many people’s work computers.
The advantages of virtual machines are separated from the rest of the system. This means that the software inside the VM cannot interfere with the host computer’s primary operating system.
From the user’s perspective, the VM works like a bare metal machine. In most cases, a user connecting to a VM is unaware that it is a virtual environment. Guest operating systems and their applications can be configured and updated as needed, and new applications can be installed or removed without affecting the host or other VMs.
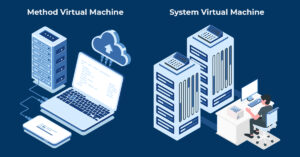 VMs are often classified by the type of hypervisor that manages them or the type of workload they support. However, VMs are also classified by VM type:
𝐏𝐫𝐨𝐜𝐞𝐬𝐬 𝐕𝐢𝐫𝐭𝐮𝐚𝐥 𝐌𝐚𝐜𝐡𝐢𝐧𝐞𝐬: A process VM is a temporary, platform-independent programming environment for running a single process as an application. This environment provides a high level of abstraction that masks the underlying hardware or operating system.
A process VM is created when a process starts and destroyed when the process ends. Two common examples of process VMs are the Java Virtual Machine, part of the Java platform, and the Common Language Runtime used for the .NET Framework.
𝐒𝐲𝐬𝐭𝐞𝐦 𝐕𝐢𝐫𝐭𝐮𝐚𝐥 𝐌𝐚𝐜𝐡𝐢𝐧𝐞𝐬: A system VM is a fully virtualized environment hosted on a physical server running its own operating system. VMs share the physical resources of the host, but provide a complete environment for running applications and services like a physical machine, but without the overhead.
A system VM relies on a hypervisor to virtualize hardware resources and make them available to the VM environment. Common examples of system VMs are those powered by virtualization platforms such as VMware vSphere and Microsoft Hyper-V.
VMs are often classified by the type of hypervisor that manages them or the type of workload they support. However, VMs are also classified by VM type:
𝐏𝐫𝐨𝐜𝐞𝐬𝐬 𝐕𝐢𝐫𝐭𝐮𝐚𝐥 𝐌𝐚𝐜𝐡𝐢𝐧𝐞𝐬: A process VM is a temporary, platform-independent programming environment for running a single process as an application. This environment provides a high level of abstraction that masks the underlying hardware or operating system.
A process VM is created when a process starts and destroyed when the process ends. Two common examples of process VMs are the Java Virtual Machine, part of the Java platform, and the Common Language Runtime used for the .NET Framework.
𝐒𝐲𝐬𝐭𝐞𝐦 𝐕𝐢𝐫𝐭𝐮𝐚𝐥 𝐌𝐚𝐜𝐡𝐢𝐧𝐞𝐬: A system VM is a fully virtualized environment hosted on a physical server running its own operating system. VMs share the physical resources of the host, but provide a complete environment for running applications and services like a physical machine, but without the overhead.
A system VM relies on a hypervisor to virtualize hardware resources and make them available to the VM environment. Common examples of system VMs are those powered by virtualization platforms such as VMware vSphere and Microsoft Hyper-V.
 The benefits of virtual machines extend the computing potential of a single device, increasing the performance and flexibility of existing hardware. Mac users who need to run Microsoft tools can use a Windows virtual machine instead of purchasing a new computer. Also, if a PC developer wants to see how his new app will look on his Mac, he can do so using a virtual machine.
➤Building and deploying apps in the cloud.
➤Back up your existing operating system.
➤Testing new operating systems (OS) including Beta.
➤You have installed an outdated operating system to access virus-infected data or run outdated applications.
➤Running software or apps on operating systems for which they were not originally intended.
➤Set up new environments to help developers run development test scenarios easier and faster.
Enterprises are also looking to VMs as an additional layer of security to provide against potential threats. If your VM is compromised, you can delete it or revert to a recent backup or snapshot. The threat is isolated to that VM because it is isolated from the host and other VMs.
Enterprises often deploy VMs when they want to run multiple applications simultaneously that require different operating systems and computing power. For instance, your quality assurance team wants to test multiple web servers and small databases simultaneously, or your IT department needs to use the same server to run graphics-intensive gaming software and customer service databases. there is.
DevOps can also leverage VMs for continuous integration and delivery operations. Or, your organisation may need an environment to run legacy applications alongside other workloads.
The benefits of virtual machines extend the computing potential of a single device, increasing the performance and flexibility of existing hardware. Mac users who need to run Microsoft tools can use a Windows virtual machine instead of purchasing a new computer. Also, if a PC developer wants to see how his new app will look on his Mac, he can do so using a virtual machine.
➤Building and deploying apps in the cloud.
➤Back up your existing operating system.
➤Testing new operating systems (OS) including Beta.
➤You have installed an outdated operating system to access virus-infected data or run outdated applications.
➤Running software or apps on operating systems for which they were not originally intended.
➤Set up new environments to help developers run development test scenarios easier and faster.
Enterprises are also looking to VMs as an additional layer of security to provide against potential threats. If your VM is compromised, you can delete it or revert to a recent backup or snapshot. The threat is isolated to that VM because it is isolated from the host and other VMs.
Enterprises often deploy VMs when they want to run multiple applications simultaneously that require different operating systems and computing power. For instance, your quality assurance team wants to test multiple web servers and small databases simultaneously, or your IT department needs to use the same server to run graphics-intensive gaming software and customer service databases. there is.
DevOps can also leverage VMs for continuous integration and delivery operations. Or, your organisation may need an environment to run legacy applications alongside other workloads.

Join over 150,000+ subscribers who get our best digital insights, strategies and tips delivered straight to their inbox.
One reply on “How Do Technologies Such As Virtual Machines Help To Improve IT Productivity and Efficiency?”
Very helpful