 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Grok
Grok
 Perplexity AI
Perplexity AI

4 min read | By Postpublisher P | 28 December 2023 | Blockchain
Delivering the necessary decentralisation to the FinTech sector, Decentralised Finance has emerged as an important component of the crypto space.
From giving the liberty to the masses to control their finances to simplifying the process of lending, DeFi has found many use cases through dedicated applications. According to BCC research, the global market size for DeFi is projected to stand at $70.3 billion for the forecast period 2022-2027 while making its way through investments, market-making, trading, and more.
The goal behind Decentralized Finance is to challenge and eventually replace the flaws of traditional financial services. Harnessing open-source code through blockchain programming languages, DeFi allows anyone with the opportunity to build on pre-existing applications in a permissionless, composable manner.
In other words, decentralized finance, or DeFi, has emerged as a transformative force redefining the blockchain and cryptocurrency landscape. In this comprehensive guide, we will dive through various aspects of DeFi, how it works, its key components, the potential use cases, and the risks involved.
Let’s dive in.
At its core, DeFi stands for decentralized finance. It harnesses the power of blockchain technology to create a financial ecosystem where users can access financial services without relying on traditional intermediaries like banks.
Unlike conventional solutions, DeFi operates 24/7, ensuring transactions occur in near real-time while giving no control access to any personnel, organization, or authority. It means no central authority can halt or control the network at any point in time.
The driving force behind DeFi is the utilization of smart contracts. These are the self-executing contracts containing the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller directly written into code. Smart contracts are made to smoothen the financial operation while complementing a variety of financial activities such as lending, borrowing, trading, and yield farming.
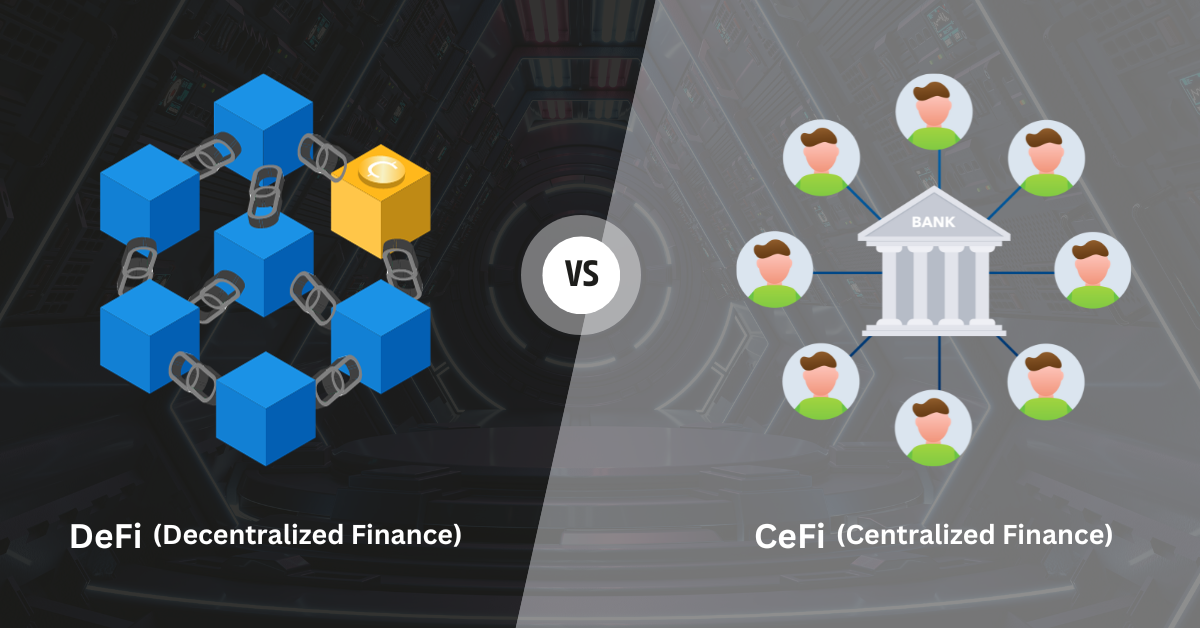
To appreciate the significance of DeFi, it’s crucial to compare it to centralized finance (CeFi).
In the world of CeFi, commercial banks play a central role, offering services such as storing money, lending capital, and facilitating transactions. While these institutions provide a proven track record and security measures, they also exert control over users’ assets and have operational limitations.
In contrast, DeFi empowers users by allowing them to access financial services directly through blockchain technology. Decentralization eliminates the need for intermediaries, making DeFi services accessible to anyone with an internet connection.
It means users can store their assets securely and enjoy round-the-clock access. DeFi offers the unbanked population a chance to access financial services that were previously beyond their reach.
The DeFi ecosystem comprises various components, each playing a vital role in creating a decentralized financial system. Therefore, it is necessary that every element of the DeFi ecosystem must be understood to ensure effective blockchain development services and learn how the entire DeFi setup works.
⒈ Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): DEXs allow users to trade digital assets directly without intermediaries, enhancing security and control over their funds. Popular DEXs like Uniswap and SushiSwap have gained immense popularity.
⒉ Aggregators and Wallets: Aggregators streamline users’ interaction with the DeFi market, automatically optimizing their asset allocation for maximum returns. On the other hand, wallets are essential for storing and transacting digital assets, with users having the option of self-hosted or exchange-based wallets.
⒊ Decentralized Marketplaces: Decentralized marketplaces are the platforms that enable users to engage in trustless peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries. A quick example of the same can be Ethereum, which among other blockchains, hosts numerous decentralized marketplaces.
⒋ Oracles and Prediction Markets: Oracles provide real-world data to smart contracts, enabling prediction markets where users can bet on event outcomes. These platforms automate payouts through smart contracts.
⒌ Layer 1 Blockchains: DeFi solutions run on various layer-1 blockchains, with Ethereum being the most prominent. Competing blockchains like Polkadot, Tezos, Solana, BNB, and Cosmos are used simultaneously to gain scalability and innovation opportunities.
DeFi has witnessed tremendous growth, offering innovative use cases that challenge traditional finance. These involve everything from lending, payments, margin trading, yield farming, liquidity provision, decentralized exchanges, stablecoins, and prediction markets, enhancing financial accessibility. Some of the key DeFi applications could be highlighted as:
⒈ Lending Platforms: DeFi lending protocols allow users to borrow funds against their cryptocurrency collateral, with billions of dollars locked in these platforms.
⒉ Payments and Stablecoins: Stablecoins, pegged to fiat currencies, provide stability in a volatile crypto market, facilitating transactions and lending within DeFi.
⒊ Margin and Leverage: DeFi introduces margin trading, allowing users to borrow cryptocurrencies on margin, amplifying potential returns. However, it also increases risk due to algorithm-based systems.
⒋ DeFi-Native Activities: Liquidity pools and yield farming enable users to earn returns by providing liquidity to decentralized exchanges, enhancing the DeFi experience.
While DeFi offers immense potential to the FinTech sector while enabling users across the globe to take control of their finances, it has its own significant risks that are required to be worked.
⒈ Scalability Issues: Blockchains are required to be made more scalable to support DeFi’s growing user base, as transaction speeds can be sluggish.
⒉ Regulatory Uncertainty: The regulatory environment for DeFi remains unclear, with governments worldwide attempting to fit DeFi into existing frameworks or create new regulations.
⒊ Security Concerns: Like any other digital venture that runs on the digital agenda, DeFi platforms are likely to face hacks, emphasizing the need for robust security measures.
People make money with DeFi through various strategies. One common approach is providing liquidity to decentralized exchanges (DEXs) or lending platforms. It involves depositing their cryptocurrencies into smart contracts, which are then used for trading or lending.
In return, liquidity providers receive a portion of the fees generated from these transactions. Another way is through yield farming, where users lock up their assets in DeFi protocols to earn rewards, often in the form of governance tokens. These tokens can be staked, traded, or sold for profit. Additionally, users can participate in staking, where they lock up their tokens to secure the network and receive rewards in return.
Moreover, some individuals engage in margin trading, leveraging their assets to amplify potential gains (although this comes with higher risk). Others participate in DeFi governance, influencing protocol decisions and earning rewards for their participation.
DeFi is reshaping the financial landscape, offering accessible and permissionless financial services. As the DeFi space continues to evolve, it presents both opportunities and challenges to blockchain development services providers as well as the end users.
Therefore, it is vital that users should exercise caution, conduct thorough research, and stay updated on the latest developments in this exciting and rapidly evolving sector. After all, DeFi contains all the potential needed to revolutionize finance, empowering individuals globally with financial freedom and autonomy.
Good Luck!
Join over 150,000+ subscribers who get our best digital insights, strategies and tips delivered straight to their inbox.