 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Grok
Grok
 Perplexity AI
Perplexity AI

4 min read | By Nishali M | 13 January 2026 |
Source: Precedenceresearch
Cloud-native development is mainly driven by the interest in serverless computing. It transforms the way modern applications are created, deployed and scaled. What started with simple FaaS architecture has grown into a broad ecosystem of managed services, event-driven computing, and scalable cloud systems. Serverless has evolved far beyond functions and users in a completely new era of efficiency, automation and innovation for enterprises of all sizes.
Serverless architecture does not only play a role in lessening the workload of infrastructure management, but also provides benefits to the developers by letting them deliver quicker, test their ideas without any limitations and restore old applications with very little effort. Furthermore, its ability to work together with microservices, containers and cloud-managed databases makes it the basic element of modern cloud development. While companies are gradually moving to the cloud, serverless re-architecting, securing and optimizing applications thus enabling highly agile, resilient and cost-efficient digital ecosystems.
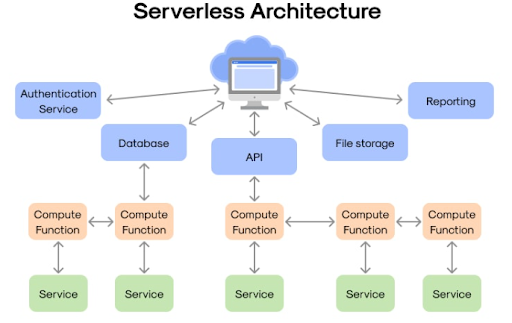
Serverless computing is an execution model of the cloud where developers build and run applications without ever managing underlying servers. The cloud provider is responsible for automatic infrastructure provisioning, scaling, patching, and maintenance. Technically, servers exist, but to the user, they are invisible, which removes a big layer of operational overhead.
In serverless, everything, fromcomputing and storage to networkingand runtime environments, is handled by the cloud provider. This frees the developer to work purely on writing business logic, not the management of infrastructure.
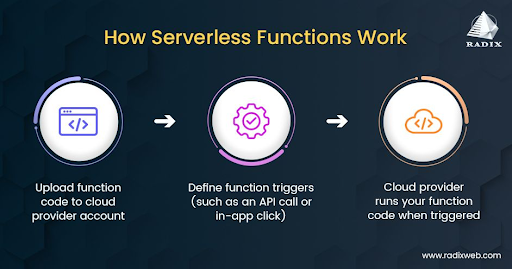
It enables programmers to run code without thinking about servers or infrastructure; it runs the code when it needs to and scales the resources automatically according to demand. Behind serverless is an event-driven architecture.
These events could be triggered by an activity such as API calls, file uploads, changes to a database, or queue messages.
Services like AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, and Google Cloud Functions instantly allocate the appropriate amount of computing resources for any event. Functions run in a fully managed environment, with no server setup, patching, or maintenance required.
The system scales up automatically during high demand and scales down to zero when idling.
That is, infrastructure, scaling, networking, and availability are taken care of by the cloud provider, minimizing the operational overhead.
This means the developers can stay laser-focused on writing code and integrating it with other cloud-native services.
Serverless development is gaining a lot of attention from modern companies because of its unbeatable flexibility, scalability and cost reduction. These are the main advantages of using serverless service:
Serverless architecture patterns scale automatically in accordance with the demand of the application, hence, it is capable of expanding and reducing the computing resources in real time, regardless of whether the application is receiving one request or millions.
In serverless cost optimization, pricing is based on the time of the execution of functions or events and not on idle infrastructures. That makes it particularly useful when workloads are either hard to predict or variable.
Cloud provider takes care of everything such as server management, patch application, and underlying compute cluster monitoring, which allows teams to focus on enhancing features and user experience.
Serverless eliminates infrastructure constraints, thus developer’s deployment of features is done at a quicker pace. This not only speeds up the whole process of innovation but also makes serverless perfect for agile teams and growing businesses.
It removes low-level infrastructure management tasks and allows developers to direct their efforts to logic, microservices design, and user experience improvement.
By design, serverless platforms include multi-region redundancy, seamless failover, and automatic error recovery that enhance application resiliency.
| Feature | Serverless | Containers |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure Management | Cloud provider Fully managed: no server setup or maintenance required | Requires management of container runtime and orchestration platform, such as Kubernetes |
| Scaling | Automatic, event-driven scaling; can scale to zero when idle | Can scale dynamically, but usually requires manual setup or orchestration. |
| Billing & Cost Efficiency | Pay for the execution time or resources consumed alone; highly cost-effective. | When running instances are charged, there is a possibility of incurring idle costs as the usage is not considered. |
| Use Cases | Event-driven tasks, microservices, APIs, and short-lived workloads are some of the major use cases. | While others like the long-running applications, microservices, and predictable workloads are also in the category of use cases. |
| Operating Overhead | Lowest; just code and logic left to focus on | Overhead; the full management of deployment, updating, and scaling needed. |
| Environment Control | Very limited: The provider restricts the runtime environment. | The user is in full control of this environment, from libraries to dependencies. |
| Startup Time | Generally very fast, and suitable for bursty workloads. | Slower but depends on when the container is ready; it varies. |
A serverless application represents a software system created in relation to the serverless computing paradigm, where management of all underlying infrastructure lies with the cloud provider. The application is based on the FaaS architecture, and by using managed services, it provides a possibility for developers to write purely business logic without server management, scaling, or maintenance.
Events are in the forms of API calls, updating the database, or uploading files.
Resources automatically scale up or down depending on demand. Cost efficiency is ensured through auto-scaling.
You pay for actual execution time and avoid unnecessary expenses.
It provides easy integration with databases, storage, messaging systems, and other services that are cloud-native.
It enables the developers to focus on coding and workflows while everything related to infrastructure management is the cloud provider’s responsibility.
Serverless computing is one of the most important developments in modern history related to software. What was initially designed as a straightforward model to FaaS has now grown to a well-rounded ecosystem of event-driven, scalable,optimized cloud services. Serverless security enables rapid innovation, reduced operational overhead, and modernization of applications with minimum complexity for organizations.Cloud-native development is getting more sophisticated every day, and serverless is still the main factor that leads to future-proofed Cloud architectures, integrating the best of scalability, efficiency, and agility for developers. Serverless is more than a technology in a world where speed and flexibility dictate the competitive advantage-it is the way to go for the next generation of digital experiences to be built.
It is auto-scaling and low management needs make it ideal for fast-moving teams.
Start by deploying small event-based functions on platforms like AWS or Google Cloud.
Serverless handles scaling for you, while containers require more hands-on setup.
It is a good fit if the app can be broken into lightweight, event-driven components.
Optimize function runtimes and pay only for actual execution time.
Join over 150,000+ subscribers who get our best digital insights, strategies and tips delivered straight to their inbox.