 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Grok
Grok
 Perplexity AI
Perplexity AI

4 min read | By Admin | 12 November 2025 |
Source: Marketsandmarkets
How does Digital Twin software support the optimization of real systems? It encompasses the ability to create exact miniature simulations of physical machines, devices, and even entire processes. These twin models can be used for continuous tracking of performance, anticipating faults, optimizing asset use, and even conducting trials on new designs or simulation models, all without jeopardizing actual physical assets.
Industries are being transformed with the introduction of Industrial IoT integration digital twins, predictive maintenance, real-time simulations, and advanced analytics. This technology supports better decisions, cost savings, efficiency improvements, and faster innovation and is critical for the manufacturing, healthcare, transportation, and software sectors.
A digital twin is the simulation of a physical entity in a virtual environment, which remains a real counterpart. It is developed using data obtained from sensors, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and other related data sources that reflect a physical entity’s behaviour, performance, and state.
Unlike static models that need to be updated manually,digital twin software is a dynamic data-driven model that helps organizations keep an eye on, analyze, and improve operations. For instance, manufacturing equipment’s digital twin helps in predicting failures long before they happen, facilitating maintenance optimization. Digital twins in healthcare provide virtual patients on whom treatments can be tested.
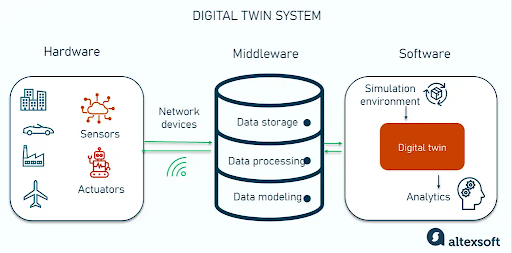
A digital model is created for, and represents, a physical object, system, or process. It has to respond not only to current information and its current analysis but also all the historical information that it consumes.
The performance, condition, and usage metrics are automatically collected and sent via sensors, IoT, and similar connected devices.
To develop a virtual model of the asset there needs to be a cloud or software platform able to accept the data
A digital twin uses artificial intelligence, analytics, and machine learning to explore what-if-analyses, predict potential situations, and proactively address issues.
The insights obtained are put to work to ensure that processes run smoothly, downtime is minimized and decisions are made confidently.
Digital twins connect the physical world to the digital offering organizations a safe environment to experiment, optimize and innovate in real-time.
Digital Twin technology can provide organizations with a more intelligent way to understand, monitor, and optimize their assets, processes, or systems. By connecting digital and physical realities it provides an abundance of benefits to organizations:
early identification of potential issues leads to less downtime and a decrease in overall costs.
offers continuous insight into the performance, status, and efficiency of an asset management.
Relies on analytical capabilities and modelling to facilitate advanced decision-making.
Reduces the cost of physical trial-and-error by conducting model alterations virtually, first.
Allows enterprises to evaluate new concepts and refine designs prior to production.
Process improvement, utilization of assets and equipment and producing reduced wasted energy.
Allows for programmatic, and therefore customizable, offerings and rapid responses through foresight of user needs.
| Industry | Example of Digital Twin |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Virtual representation of a production line to monitor equipment, detect inefficiencies, and test improvements. |
| Healthcare | Organs like the heart and lungs can be replaced by patient-specific digital twins to carry out simulated treatments for real patients and to predict health outcomes. Smart Cities |
| Smart Cities | A digital twin can be created for the entire city which can serve as a means of managing traffic, emergency response, city utilities, energy, and more. |
| Automotive & Aerospace | Cars and even aircraft can be modeled, and tested to avoid the expense of actually building physical prototypes. |
| Energy & Utilities | Wind farms and even turbines could be modeled along with entire power grids for better forecasting of demand and more efficient asset optimization. |
| Retail & Supply Chain | Digital twin of customer journey and supply chains to optimize inventory and create a more personalized shopping experience. |
The imminent changes brought to digital twins through innovations in IoT, AI, machine learning, and cloud computing are insightful to consider. Their benefits will increase, and they will become easier to use, thus enhancing more advanced features. No longer just passive observers, digital twins will evolve to become predictive, self-managing, and in real time replicate complex systems! Across all sectors, from manufacturing, health, and energy, to smart ecosystems can bet that digital twins will become everyday language as industries seek ways to increase productivity while reducing costs, time, and environmental footprints using digital twins.
The rise of cloud and edge computing often makes their scalability along with the management of large-scale systems relatively simple to implement. Digital twins may also have an even larger personal component; applications for personalized medicine and health care; personal wellbeing and planning. In the end, digital twins are bound to be the key pillar of digital transformation, facilitating enhanced insights, innovation, and a sustainable future.
The use of digital twin technologies spans multiple industries and is relevant across different verticals. It creates a compact, yet detailed, digital rendition of asset governance, allowing an unprecedented level of supervision, forecasting, and enhancement. Its use is already being noted in improving manufacturing processes and healthcare, in addition to smart manufacturing and sustainable energy systems that continue to grow in their use of digital twins.
While digital twins, as a concept, are promising, their integration with day-to-day and specialized operations is unprecedented. For example, cutting-edge innovation, operational improvements, and cost-cutting measures can be realized, and some of these may already be implemented through real-time data bridging and monitoring via digital twins. Their use is especially crucial in today’s context, where sustainable operations, AI, cloud computing, and IoT are the need of the hour, and digital twins can deeply impact organizational structure.
Join over 150,000+ subscribers who get our best digital insights, strategies and tips delivered straight to their inbox.